January 25 2026 at 08:00AM
Falcon 9 – The ESG Workhorse of SpaceX
Best Practices / Lessons Learned
Space exploration is no longer just an ambitious quest for humanity's future among the stars; it now carries responsibilities tied to sustainability, efficiency, and global collaboration. The Falcon 9, SpaceX’s flagship reusable rocket, masterfully combines innovation with Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) values, making it a beacon for responsible aerospace engineering. This article delves into what makes Falcon 9 the Workhorse of ESG sustainability, explores its relevance to project managers, and delivers critical takeaways for professionals striving to balance innovation with responsibility. As usual I will help connect the dots for why this matters to project professionals and some specs on the SpaceX operations to bring you up to speed on the 589 successful missions this far.
What is the Falcon 9? 🚀🧑🏿🎤
Falcon 9, developed by SpaceX, is a two-stage rocket designed primarily to transport satellites and cargo—and eventually humans—into orbit. It became operational in 2010 and has since redefined the aerospace industry through its pioneering reusable technology. Unlike traditional expendable rockets, Falcon 9 is designed to return its first stage back to Earth for refurbishing and reuse(as seen in the two photo above left side with metal grate-like flaps). This capability drastically reduces costs while advancing space missions from both economic and environmental perspectives.
Capable of launching payloads into various orbits, Falcon 9 has completed over 589 missions (as of Jan. 12, 2026) with remarkable success. Its core contribution lies in normalizing rapid reusability as the standard for reducing the need to rebuild rocket components for each mission. Not only has it revolutionized access to space, but it also serves as a vessel for collaborative global endeavors, carrying satellites for governmental, commercial, and scientific purposes. According to NSF App and SpaceX.com, the rocket costs about $69.75 million to manufacturer. The Workhorse is about 83 meters tall and 8.9 meters in diameter when including both the rocket and fairing stages. In the two-part image above, you can see the detached fairing stage retuning to earth. In the diagram located on SpaceX.com, you can see the full process of the fairing stage detachment and how it flips its self to then engage a thruster before hovering over a launch pad to safely launch back to earth for reuse, as mentioned.
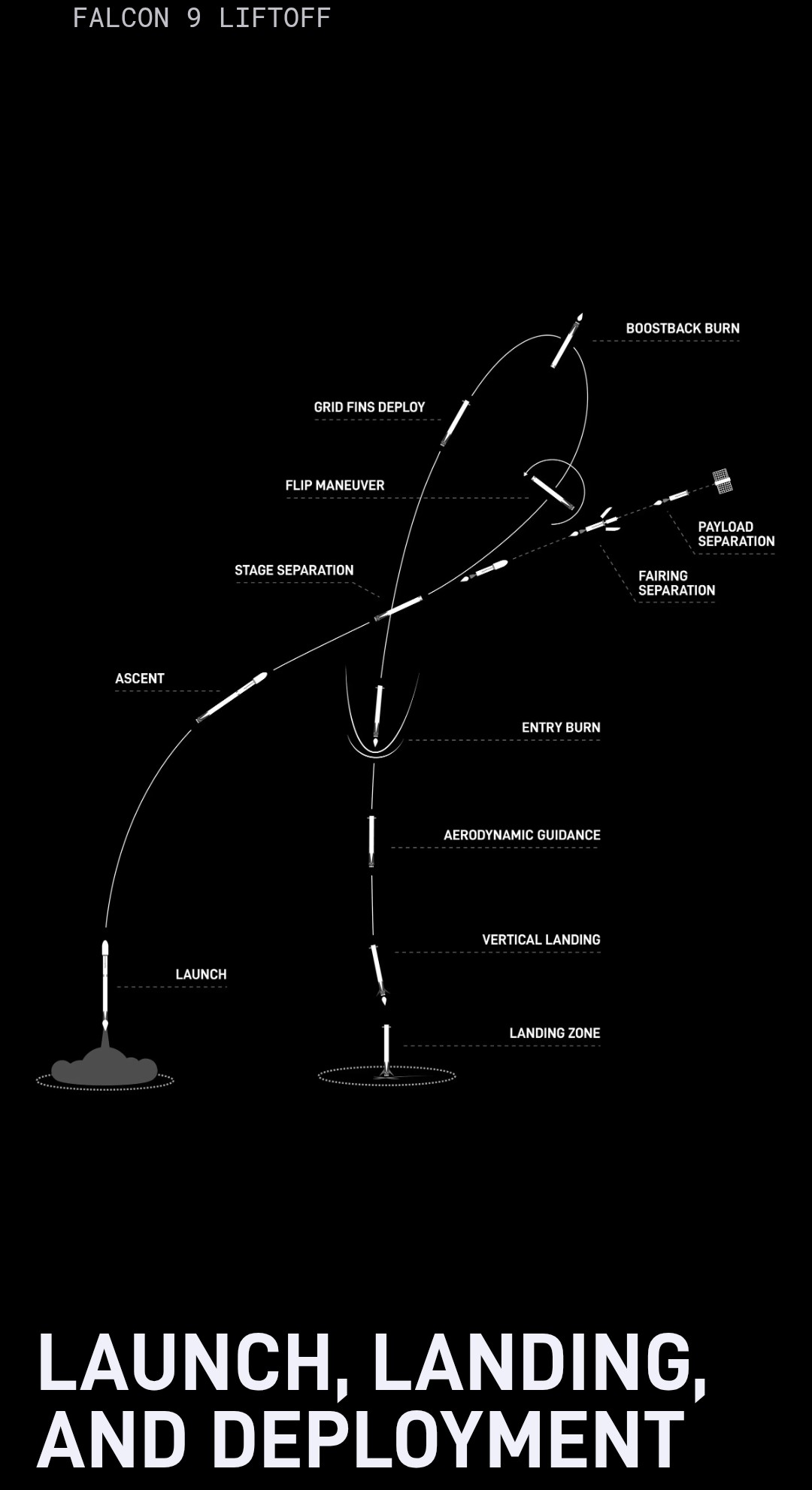
ESG Sustainability ♻️
The Falcon 9 stands tall in terms of its alignment with ESG principles:
1. Environmental Responsibility: Reusability lies at the heart of Falcon 9's contribution to environmental sustainability. Traditional rockets are often discarded after a single use, leaving behind debris and consuming significant raw materials for manufacturing new stages. Reusing the first stage key components minimizes waste and conserves materials, directly addressing environmental concerns.
Additionally, SpaceX invests in reducing the carbon footprint of its launches. While no rocket can yet claim net-zero emissions, strides are being made toward developing greener propulsion technologies and offsetting environmental impacts.
2. Social Progress: Falcon 9 democratizes access to space by significantly reducing transportation costs for payloads. This has enabled multiple nations and organizations with limited budgets to participate in satellite deployment and scientific exploration. What I love about the NSF App is it shows each launch mission, not just from United States, but each of these nations, such as China, India, Kazakhstan, and Brazil. Spurring innovation through collaboration, the rocket platform fosters global interconnectedness, bridging gaps in technological development and improving remote access to modern communication tools. I suggest researching just how make Starlink are in low orbit above your head right now as you read this article. You will be shocked ! Elon has been stated to mention that these are used for new connectivity speeds for broadband Internet so helps compensate the team when consumers use their internet services. We can also be sure that Tesla cars, and products also get data from these missions, which boosts the overall portfolio.
3. Governance and Ethics: SpaceX operates on the principle of iterative design, constantly upgrading Falcon 9 based on data from previous missions. These improvements are shared widely within aerospace communities, setting benchmarks for governance in engineering and operational transparency. Ethical considerations, such as prioritizing mission reliability and safety, underpin every Falcon 9 launch.
Through the Falcon 9, ESG sustainability is not just a byproduct but an actively integrated component of SpaceX’s vision.
Why This Matters to the PMP 🎯
For project managers, particularly those certified with PMI credentials, Falcon 9 stands as a case study in applying ESG principles to large-scale, high-risk innovations. Such projects involve an intricate balance of financial constraints, timelines, risk management, and stakeholder alignment. Falcon 9’s success provides lessons in several PMP-relevant domains:
Risk Management: The reusability model inherently brings engineering and operational risks that require rigorous testing and contingency planning. Falcon 9's iterative approach to reducing failure rates is a prime example of proactive risk management.
Innovation Under Resource Constraints: A reusable rocket maximizes value from finite resources, mirroring how project managers must achieve project objectives within resource limits while minimizing waste.
Stakeholder Inclusion: The inclusivity Falcon 9 enables—opening space to a broader array of global players—is a lesson in addressing the diverse and evolving needs of stakeholders.
Integrating sustainability into project processes is no longer optional; ESG considerations are part of the organizational mandate across industries. Project managers must rethink how they can incorporate such values into their practice, reflecting SpaceX's pioneering example.
Key Takeaways 📔📑
1. Falcon 9 exemplifies how reusable innovation can transform industries while advancing ESG objectives, including waste minimization, global collaboration, and ethical governance.
2. Reusability emphasizes the importance of iterative improvement, where lessons learned guide refinements—an essential project management practice.
3. SpaceX’s success with Falcon 9 demonstrates how cost control and sustainability need not exist in isolation but can serve mutually beneficial goals.
4. Project managers should model ESG integration into their own industries, focusing on minimizing resource impacts while ensuring stakeholder value. Effectively managed projects can drive meaningful industry change, drawing inspiration from groundbreaking initiatives like Falcon 9.
Final thought for the project professional 🤔
Falcon 9 has launched us to new heights—both literally and figuratively—proving that sustainability is inseparable from innovation. For project managers, it is an enduring reminder that a responsible and systemic approach can be just as groundbreaking as the technology itself.
I encourage you to download the NSF app to see the next live launch from Cape Canaveral in Space Coast Florida. After a few times of watching the T-minus milestones from:
"Go for prop load(T-minus 00:38)" to
"F-9 START UP (T-minus 01:00)" to
"Lift off (T-minus 00:03)"
You will begin to understand the patterns that allow for space flight and become more knowledgeable in how spaceflight works!
Sources 📰
SpaceX.com
NSF App (Next Space Flight)




